Fiberglass Wound Tube VS FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) Pipe
Fiberglass-reinforced products are widely used in power equipment manufacturing, industrial pipeline engineering, and...
Fiberglass-reinforced products are widely used in power equipment manufacturing, industrial pipeline engineering, and the composite-materials sector. Although Fiberglass Wound Tubes and FRP/GRP Pipes both belong to fiberglass composite materials, they differ significantly in structure, mechanical properties, electrical characteristics, and application scenarios.
To help engineers, purchasers, and technical users choose the right product quickly, this article provides a comprehensive comparison.
I. Definition Differences
Fiberglass Wound Tube
Manufactured by continuous filament winding (cross-angle + hoop winding) followed by resin impregnation and curing.
Features: High structural precision and high strength; suitable for electrical-insulation components.
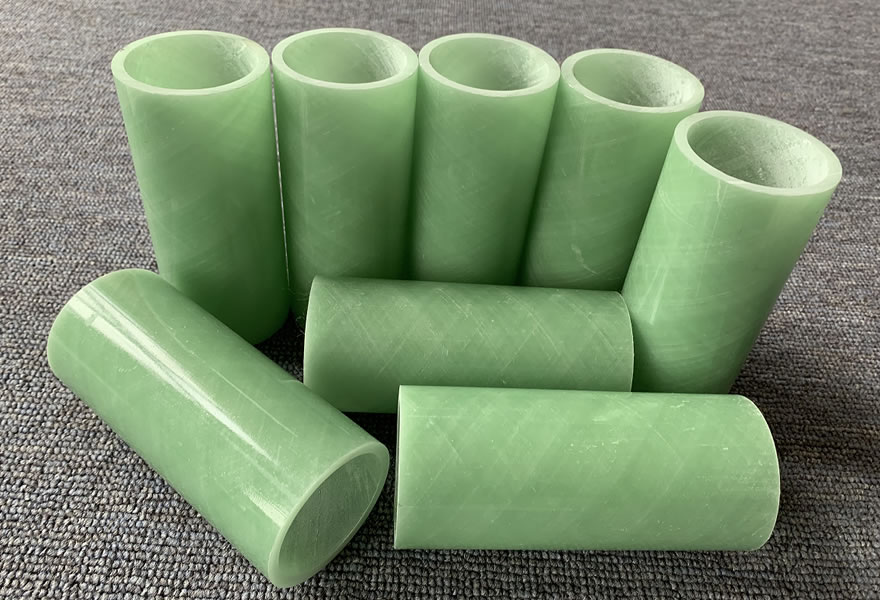

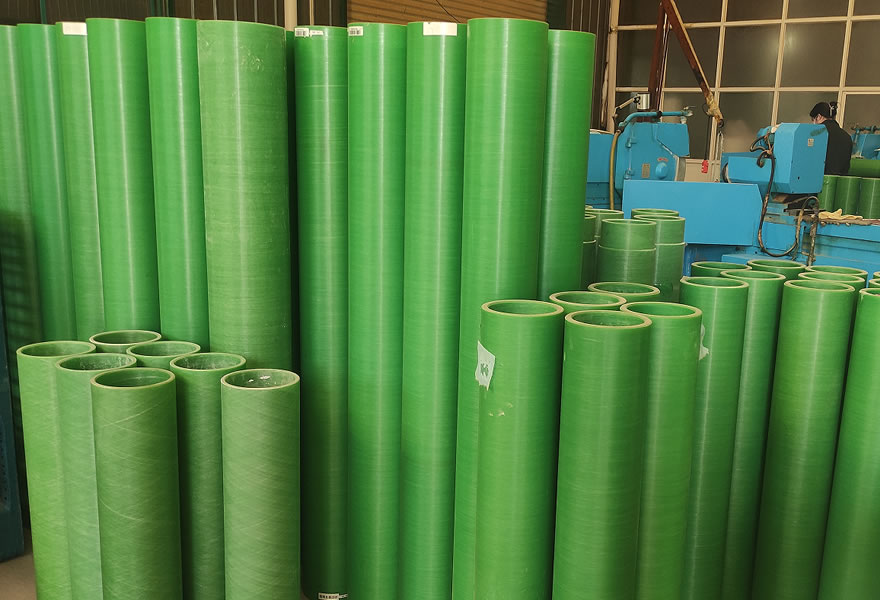
FRP Pipe (FRP / GRP Pipe)
Typically produced by filament winding, centrifugal casting, or pultrusion, and mainly used in water transmission, chemical pipelines, gas transport, etc.
Features: Focuses on corrosion resistance and mechanical performance for pipeline applications; not primarily designed for high electrical performance.

II. Performance Comparison Table (Ideal for product pages)
| Indicator | Fiberglass Wound Tube | FRP Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Structure Method | Precisely oriented continuous winding, accurate fiber distribution | Winding/spraying/centrifugal molding, more random fiber orientation |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher strength—especially axial & hoop strength | High strength but mainly for pipeline pressure requirements |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision: ±0.1–0.3 mm | Relatively lower precision |
| Electrical Insulation Performance | Excellent (high dielectric strength) | General; not specifically for electrical insulation |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent (used in chemical and seawater pipelines) |
| Heat Resistance | Stable; suitable for electrical equipment | Varies depending on resin system |
| Water Absorption | Very low | Slightly higher |
| Weight | Light | Light |
| Common Applications | Lightning arrester housings, transformer insulating supports, electrical insulation parts | Water transmission, chemical pipelines, sewage systems, underground pipe networks |
| Customizable Electrical Properties | Yes | No |
III. Key Difference Summary (One-Sentence Version)
Fiberglass Wound Tubes focus on electrical insulation and high strength precision; FRP Pipes focus on corrosion resistance and pressure performance for engineering pipelines.
IV. Differences in Power-Industry Applications
Fiberglass Wound Tube
Used for lightning-arrester housings, insulating pull rods, and high-voltage equipment structural components.
Requires electrical strength ≥ 18–25 kV/mm.
FRP Pipe
Rarely used directly in high-voltage insulation due to less stable electrical properties and higher water absorption.
V. Selection Recommendations
Choose Fiberglass Wound Tube if your application involves:
✔ Lightning arresters
✔ Switchgear
✔ Transformers
✔ Insulation supports
Choose FRP Pipe if your application involves:
✔ Chemical pipelines
✔ Water supply & drainage
✔ Seawater desalination
✔ Engineering transmission pipelines
Leave us a message to get quotation and sample!
If you are interested in our products,, please send us a message and we will contact you as soon as we receive it. Email: info@ztaero.com whatsApp: +8616650273778
Releated News
- 03-03 2026G10 Fiberglass Density Standard
- 03-02 20262026 Global Epoxy Sheet Market Trends | FR4 & G10 Electrical Insulation Demand Growth
- 02-28 2026Pultruded Epoxy Rod Applications in Power Equipment
- 02-27 2026How to Select the Thickness of Transformer Crepe Paper
- 02-26 2026ESD FR4 sheet vs Standard FR4 Epoxy Sheet
- 02-25 2026Phenolic cotton cloth rod applied to transformers