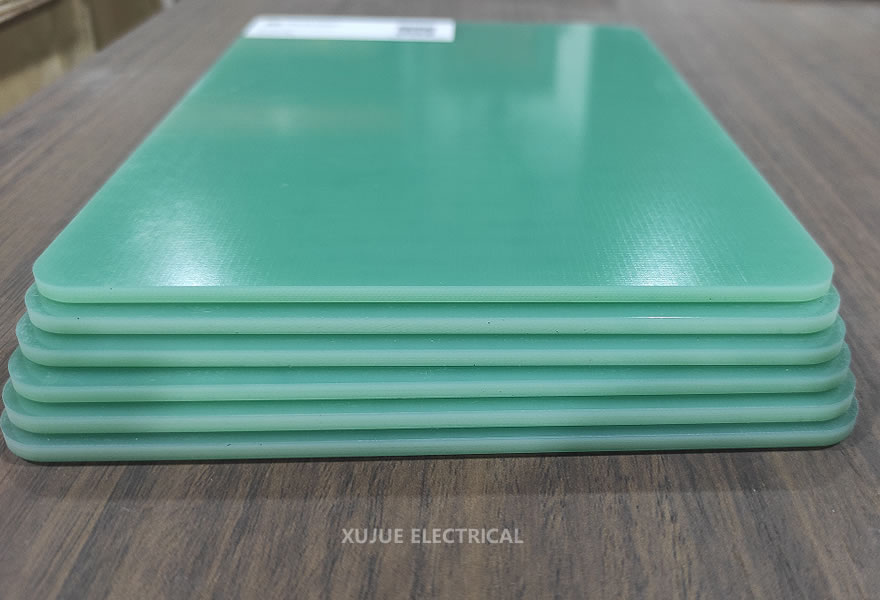
Flame-Retardant Epoxy Laminates: Properties and Flame-Retardant Mechanisms
Flame-retardant epoxy laminates are composite sheets made with epoxy resin as the base material. By adding flame retardants or using inherently flame-retardant resins, and reinforcing them with glass-fiber cloth through hot-press molding, the material can achieve specific flame-retardant ratings (such as UL94 V-0). The following provides a detailed explanation from four aspects: definition, core properties, flame-retardant principles, and application areas.

I. Definition
Flame-retardant epoxy laminates are composite materials based on epoxy resin, manufactured by incorporating flame retardants or using flame-retardant epoxy resins and reinforcing them with glass-fiber cloth via hot-pressing. Their key advantage is that, while retaining the insulation, heat resistance, and mechanical strength of conventional epoxy laminates, they also meet specified flame-retardant standards (e.g., UL94 V-0), effectively suppressing flame spread during combustion.

II. Core Properties
Flame-Retardant Performance
By adding phosphorus-based, nitrogen-based, or inorganic flame retardants, or by using flame-retardant epoxy resins, the material forms a dense char layer during burning. This layer blocks oxygen and slows heat transfer. For example, epoxy laminates with phosphorus-based flame retardants generate a non-flammable phosphoric liquid film during combustion, which further dehydrates and carbonizes into a protective carbon layer, significantly reducing the burning rate.
Heat Resistance
They can operate stably for long periods at 130 °C, with short-term heat resistance reaching 180 °C or even higher, meeting the requirements of high-temperature working conditions.
Mechanical Properties
Typical values include a through-thickness (vertical) flexural strength ≥ 340 MPa, compressive strength ≥ 350 MPa, and impact strength ≥ 33 kJ/m², enabling the material to withstand mechanical stress without deformation.
Electrical Properties
With a volume resistivity exceeding 10¹⁵ Ω·cm and stable dielectric performance, the material maintains excellent insulation even after water immersion, making it suitable for high-voltage electrical environments.
III. Flame-Retardant Principles
Flame-retardant epoxy laminates achieve flame resistance through the following mechanisms:
Char Layer Formation
During combustion, flame retardants decompose to release non-flammable gases (such as CO₂ and NH₃), which dilute oxygen concentration. At the same time, a dense char layer forms on the material surface, acting as a barrier to oxygen and heat transfer.
Free-Radical Quenching
Phosphorus-based flame retardants capture active free radicals (such as ·OH and ·O) in the combustion zone, interrupting the chain reactions of burning and reducing the combustion rate.
Synergistic Effects
Some flame-retardant systems work through multiple mechanisms simultaneously. For example, phosphorus–nitrogen synergistic flame retardants combine char formation and free-radical quenching, significantly enhancing flame-retardant efficiency.
IV. Application Areas
Electronics and Electrical Industry
Used as insulating structural components for switches, FPC stiffeners, carbon-film printed circuit boards, and transformer insulation boards to prevent electrical fires. For instance, in distribution cabinets, flame-retardant epoxy laminates can effectively inhibit flame spread caused by electrical arcing.
New Energy Vehicles and Energy Storage
Applied in battery packs as cell spacers and top protective layers to block thermal runaway chain reactions. Tests show that battery modules using 4 mm flame-retardant epoxy laminates can extend thermal runaway propagation time to 5.6 times that of modules without separators.
Rail Transit and Aerospace
Used as insulation boards and structural components in high-speed trains and aircraft, meeting both lightweight and fire-safety requirements. For example, G11 epoxy laminates, with a UL94 V-0 flame-retardant rating, are widely used in aircraft interiors and electrical systems.
Industrial Equipment
Applied in motor insulation components, grinding gears, and tooling fixtures, maintaining stable performance in humid or high-temperature environments. For instance, 3240 epoxy laminates, with a temperature resistance of 120–130 °C and a dielectric strength of 10 kV, are widely used for Class B motor insulation.