Electrical Pressboard: Density Classification and Specifications
Introduction to Electrical Paperboard Electrical paperboard is a high-quality insulating material made from speciall...
Introduction to Electrical Paperboard
Electrical paperboard is a high-quality insulating material made from specially processed cellulose fibers. It is widely used in electrical equipment for its excellent dielectric, mechanical, and thermal properties.
Classification of Electrical Pressboard by Density
Electrical pressboard is usually categorized according to its density (g/cm³), as different densities provide different mechanical and electrical properties:
Low-density pressboard
Density: 0.70–0.90 g/cm³
Features: Soft, flexible, easy to bend; suitable for low-stress areas and curved insulation.
Medium-density pressboard
Density: 0.90–1.00 g/cm³
Features: Balanced mechanical strength and flexibility; most widely used, applied in layer insulation and spacers of oil-immersed transformers.
High-density pressboard
Density: 1.00–1.20 g/cm³
Features: High mechanical strength, excellent compressive resistance; mainly used for structural components (spacers, end rings, clamping parts) in large-capacity transformers.
Ultra-high-density pressboard
Density: ≥1.20 g/cm³
Features: Very high strength, low shrinkage, good dimensional stability; used in critical parts of high-voltage and large-scale transformers.
Common Standards
Both international and national standards define density and performance requirements for electrical pressboard:
IEC 60641 – Pressboard and presspaper for electrical purposes
Defines classification, density, oil absorption, dielectric strength, etc.
High-density pressboard generally requires density ≥1.0 g/cm³.
IEC 60763 – Specification for laminated pressboard for electrical purposes
Mainly specifies laminated pressboard.
GB/T 5019-2008 – Electrical pressboard (China National Standard)
Provides detailed requirements on density, oil absorption, dielectric strength, and moisture content.
DIN 7733 (German Standard)
Specifies density ranges and mechanical strength classification.
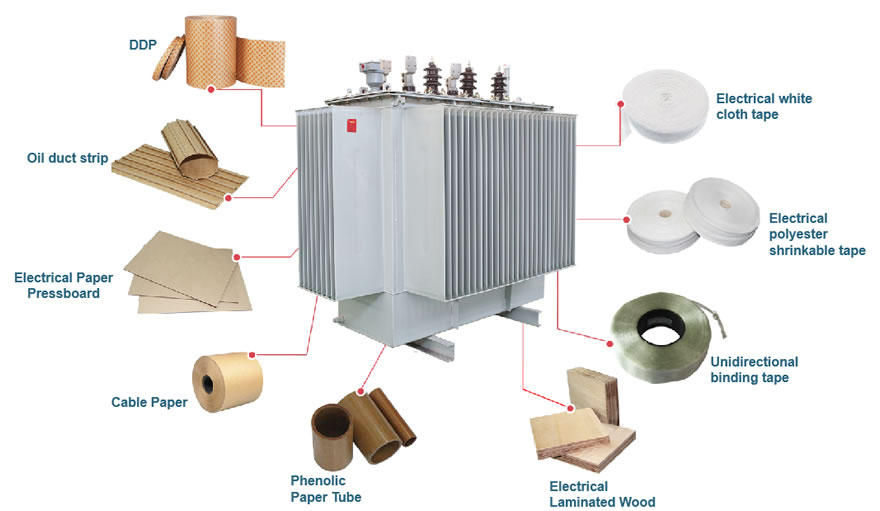

Application & Selection Guidelines
Low-density: for flexible, bendable insulation parts.
Medium-density: the most commonly used, suitable for general transformer insulation.
High/Ultra-high-density: for components under high mechanical stress and voltage, such as end rings, spacers, and clamping boards.

Classification and Selection of Electrical Pressboard by Density
| Category | Density Range (g/cm³) | Key Features | Typical Applications | Selection Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-density pressboard (Soft / Low Density) | 0.70 – 0.90 | Soft, flexible, easy to process | Coil end spacers, curved insulation parts, low-voltage equipment | Suitable for parts requiring bending and forming; not recommended for load-bearing components due to low mechanical strength |
| Medium-density pressboard (Medium Density) | 0.90 – 1.00 | Balanced strength and flexibility, good oil absorption | Layer insulation in oil-immersed transformers, spacers, coil separators | Most widely used density grade; offers comprehensive performance for general insulation parts |
| High-density pressboard (High Density) | 1.00 – 1.20 | High mechanical strength, good compressive resistance, stable performance | End rings, clamping boards, spacers, structural components in large-capacity transformers | Recommended for parts under high mechanical stress and high voltage requirements |
| Ultra-high-density pressboard (Ultra-high Density) | ≥1.20 | Very high strength, excellent dimensional stability, low shrinkage | Critical parts in extra-high-voltage or large transformers, such as support structures, end rings, clamping parts | Higher cost; usually applied in EHV and large-scale equipment only |
Selection Summary
By mechanical stress: Low/medium density for low-stress areas; high/ultra-high density for heavy-load structural parts.
By voltage level: The higher the voltage, the higher the density required.
By processing needs: Low/medium density for parts requiring bending and cutting; high/ultra-high density for compression-resistant structural components.
Leave us a message to get quotation and sample!
If you are interested in our products,, please send us a message and we will contact you as soon as we receive it. Email: info@ztaero.com whatsApp: +8616650273778
Releated News
- 02-10 20262026 Spring Festival Greeting | XUJUE ELECTRICAL
- 02-06 2026G11 Epoxy Sheet for Generator Slot Insulation
- 02-05 2026Fiberglass cloth Prices Continue to Rise | Sheet Product Prices May Be Adjusted
- 02-03 2026Epoxy Pultruded Rod Applications | Electrical Insulation & Structural Support
- 02-02 2026Common Insulation Materials Comparison for High- and Low-Voltage Switchgear
- 01-31 2026Differences Between G11 Epoxy Sheet and EPGC308