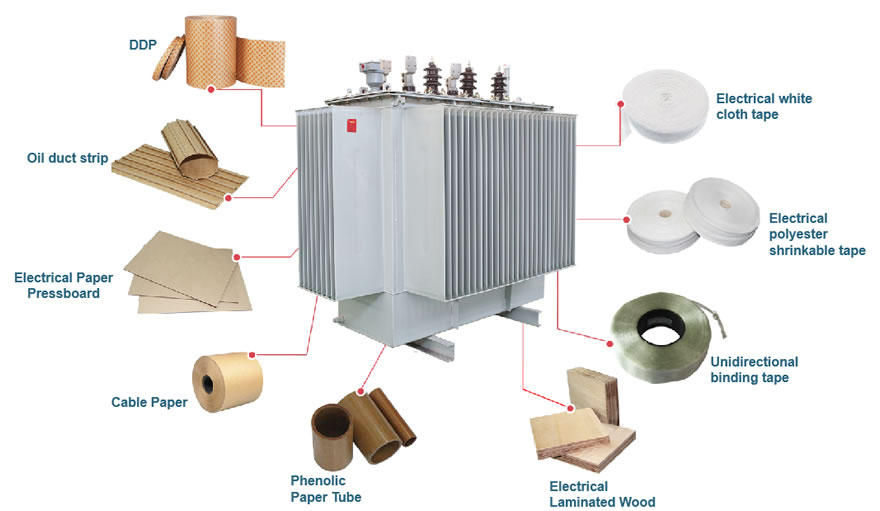
Comprehensive understanding of the main materials of distribution transformers
Comprehensive understanding of the materials used in distribution transformers 1. Insulating materials Insulati...
Comprehensive understanding of the materials used in distribution transformers

1. Insulating materials
Insulating materials are used in transformers to insulate the conductive parts from each other and from the ground (zero potential). When used in various supporting parts, they should also have good mechanical properties. In addition, insulating materials also play other roles, such as heat dissipation, cooling, fixing, energy storage, arc extinguishing, improving potential gradient, moisture-proof, mildew-proof and protecting conductors.
Under normal circumstances, insulating materials are divided into three categories:
1) Gas insulating materials: Under normal temperature and pressure, general dry gases have good insulating properties, such as air, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, sulfur hexafluoride, etc. Among them, air and sulfur hexafluoride are widely used in transformers;
2) Liquid insulating materials: Liquid insulating materials usually exist in oily form, also known as insulating oil. Such as mineral oil, vegetable oil, synthetic ester, etc.;
3) Solid insulating materials: such as insulating paint, insulating glue, insulating paper, insulating cardboard, corrugated cardboard, electrical plastics and films, electrical laminates (rods, tubes), cast epoxy resins, electric porcelain, rubber, mica products, etc.
1.1 Insulating oil
Insulating oil is characterized by high electrical strength, high lightning resistance, low freezing point, low performance temperature under oxygen, high temperature and strong electric field, non-toxic, non-corrosive, low viscosity and good fluidity. It is widely used in electrical products such as transformers, oil switches, capacitors and cables, and plays the role of insulation, cooling, impregnation and filling. In addition, it also plays the role of arc extinguishing in oil switches and energy storage in capacitors.
Insulating oil plays the dual role of insulation and cooling in transformers;
Insulating oil is currently generally divided into the following categories:
1) Mineral oil: such as transformer oil, switch oil, capacitor oil, cable oil;
2) Synthetic oil: such as dodecylbenzene, silicone oil, synthetic ester, etc.;
3) Vegetable oil;
1.2 Epoxy resin
Epoxy resin is a polymer compound. Resin is a solid, semi-solid or quasi-solid organic material with uncertain molecular weight (usually high), a tendency to flow when subjected to stress, usually a softening or melting range, and a solid cross-section that often presents a shell-like shape. It has the following basic characteristics:
1) The molecular chain is very long, each chain contains hundreds or even tens of thousands of atoms, which are covalently bonded to each other;
2) The long molecular chain is composed of the smallest repeating unit, i.e., the chain link, and the number of chain links in a molecule is called the degree of polymerization;
3) The total intermolecular force of macromolecules often exceeds the chemical bond force between atoms in the molecule, resulting in a series of characteristics in polymer compounds: for example, there is no gaseous polymer, the polymer dissolution process is very slow, etc. If there is cross-linking between molecules, this feature is more outstanding.
Epoxy resin refers to oligomers containing epoxy functional groups. Epoxy resins began to appear in 1891. After 1947, several companies in the United States and Switzerland successively synthesized bisphenol A epoxy resins industrially. my country began production in 1956.
The electrical insulation performance of epoxy materials is particularly outstanding. When no filler is added, the EB of the cured product is higher than 16MV/m, the pV is higher than 1011Ω˙m, the εr is 3-4, and the tanδ is about 0.002 at the power frequency. Therefore, 20% of epoxy resins are used for electrical and electronic insulation, such as epoxy impregnation varnish as Class B insulating varnish, impregnation of small and medium-sized motor stator windings; epoxy solvent-free varnish is used for vacuum impregnation of large motor stator windings; laminated products (plates, tubes, rods) are used as slot wedges and pads for motors, high-voltage switch operating rods; adhesives are used for bonding high-voltage porcelain bushings; casting materials are used for disc-shaped isolation insulators, mutual inductors and high-voltage ceramic capacitors in sulfur hexafluoride fully enclosed switchgear (GIS). At present, the brand names of epoxy resins or modified epoxy resins produced in China are still not very unified. The names of different epoxy resin manufacturers around the world are also different, and need to be identified according to trademarks.
Epoxy resins are only oligomers and can only be used after curing. The curing agent can react with the epoxy resin to crosslink the resin molecules from a linear structure to a three-dimensional structure. The accelerator/catalyst is an auxiliary agent that can reduce the activation energy of the reaction and can promote/adjust the gel reaction process of the casting material. The curing agent uses the active hydrogen it contains to react with the active epoxy group in the resin to achieve curing through a ring-opening addition reaction. The active hydrogen is the hydrogen in -NH2, -NH-, -C00H, -OH and -SH in the curing agent or accelerator. Commonly used curing agents are amines and anhydrides. Some curing agents require accelerators/catalysts, some require high temperature conditions, and some react violently at low temperatures. Different curing agents will also lead to great differences in the performance of the cured product, which has a significant impact on the final performance of the product. Therefore, it is very important to design and select curing agents in the epoxy resin formulation system.
Epoxy insulation is used in dry-type transformers, which is a new development in the past 40 years. The design life of the transformer coil is required to reach 30 years, and the heat resistance level reaches F level. It is difficult for general materials to meet the requirements.
To this end, the materials used and their formulation systems and processes must be designed, optimized, tested and verified to achieve the desired effect. In resin-insulated dry-type transformers, the epoxy resin system is formed by casting or dipping, and then thermally cured to form coil insulation (i.e. longitudinal insulation). During the entire operation of the dry-type transformer, the epoxy resin insulation must simultaneously ensure the electrical insulation and mechanical strength of the coil, and dissipate the heat inside the coil by heat conduction.
Its biggest weakness is the irreversibility and irreparability of resin insulation defects and damage (generally defects occur during the manufacturing process and damage occurs during operation). Therefore, it is particularly important to avoid cracking of solid insulation, avoid casting defects, and avoid partial discharge (i.e. partial discharge), which has become the key to solid insulation manufacturing technology and the focus of competition among manufacturers.
Due to the high temperature rise caused by the loss during transformer operation, the resin insulation works at high temperature for a long time (for example, the maximum operating temperature of the F-class transformer is generally designed to be around 140℃), and the transformer may be at a low temperature (such as -30℃) before commissioning and during maintenance. Moreover, the transformer may be subjected to high voltage shocks from lightning or huge electric power shocks during short circuits at any time. The coils of resin insulation should be able to adapt to these changes and resist or withstand short-circuit electric power shocks under extreme high and low temperatures. Therefore, extremely stringent requirements are placed on the thermal, mechanical and electrical properties of the epoxy insulation system.
There are currently two insulation material systems for resin cast transformers, one is “pure resin casting + high filling rate glass fiber reinforcement”, and the other is “resin quartz powder casting + pre-impregnated glass grid local reinforcement”.
The insulation system (commonly known as the insulation structure) covers a wider range than the insulation material system. It refers to the insulation of electrical equipment (or its independent components). It not only includes insulation materials and their combination methods, but also considers the relationship between insulation and conductors or magnets, the relationship with electric fields, and the relationship between insulation and the surrounding environment (gas or liquid and its conditions, surface contamination, heat dissipation conditions, mechanical forces or radiation effects, etc.). Its adaptability to the operating parameters of the power system is insulation coordination. The airflow and heat dissipation conditions in dry-type transformers, the insulation stress conditions, etc. are all within the scope of consideration of the insulation system.
1.3 Insulation paper
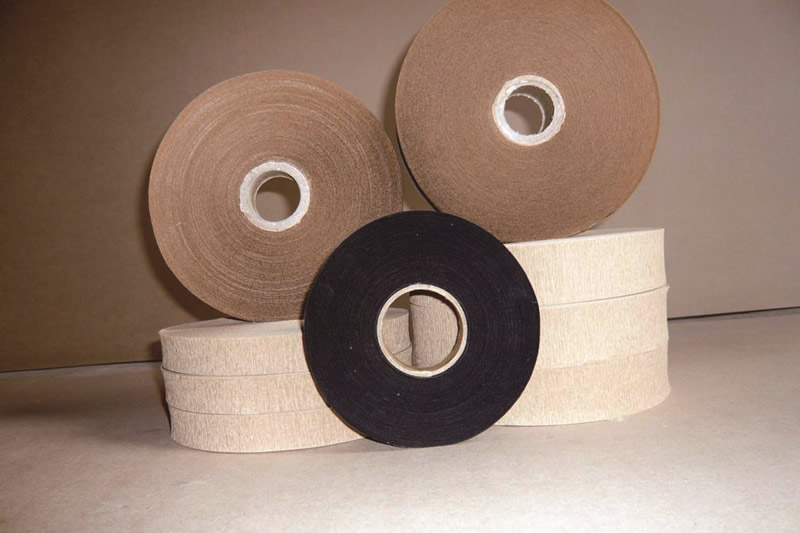
Plant fiber paper is divided into wood fiber, cotton fiber and hemp fiber. The most commonly used one is pure sulfate wood pulp fiber paper. Its raw material is wood. The commonly used one is the wood of the Pinaceae family in softwood, such as yellow pine, white pine, red fir and red pine. The main component is cellulose, which is a natural polymer compound. The manufacturing method of insulating paper adopts chemical method, such as sulfate method. In this method, the main component of cooking liquid is sodium sulfide (Na2S). Sodium sulfide is hydrolyzed to produce sodium hydrogen sulfide and sodium hydroxide. Sodium hydrogen sulfide can react with lignin other than cellulose and dissolve it in alkali solution. The cooking liquid is relatively mild, so the molecular weight of cellulose decreases very little. Commonly used plant cellulose insulating papers in transformers include: power cable paper, high-voltage cable paper and transformer inter-turn insulation paper, etc.
1) Cable paper: Cable paper is made of kraft pulp, with grades of DL08, DL12, and DL17, with thicknesses of 0.08mm, 0.12mm, and 0.17mm respectively, and is supplied in rolls. After being impregnated with transformer oil, the mechanical strength and electrical strength of cable paper will be significantly improved. For example, the electrical strength of power cable paper in air is 6-9×103kV/m, and after being dried and impregnated with transformer oil, its electrical strength reaches 70-90×103kV/m. Cable paper has sufficient thermal stability during the operation of the transformer and is usually used as winding insulation and interlayer insulation. Cable paper includes high-voltage cable paper, low-voltage cable paper, high-density cable paper, and insulating corrugated paper. High-voltage cable paper is suitable for 110-330kV transformers and mutual inductors, and has a low dielectric loss tangent value; low-voltage cable paper is used for the insulation of power cables and transformers or other electrical products of 35kV and below; insulating crepe paper is made by corrugating electrical insulating paper, with wrinkles along its transverse direction, which is pulled apart when stretched, and is often used for wrapping insulation of oil-immersed transformers, such as insulation wrapping of coil outlets, leads and electrostatic shielding devices; high-density cable paper is also a kind of insulating crepe paper, which has an electrical strength 100%-150% higher than that of ordinary crepe paper, and a mechanical strength 50% higher. It has high electrical strength, good oil resistance, good elasticity, and is easy to stretch. It can replace varnished cloth tape as insulation for leads and wire connections and bending parts.

2) Telephone paper: Telephone paper is also made of sulfate pulp and is commonly used for telephone cables. It has poor mechanical strength and is generally used as turn insulation, layer insulation or conductor covering insulation of wires.
3) Capacitor paper: Capacitor paper is divided into Class A and Class B according to the use requirements. Class A capacitor paper is used on metallized paper dielectric capacitors in the electronics industry. Class B is mainly used as the inter-electrode medium of power capacitors. Capacitor paper is characterized by high tightness and thin thickness. Capacitor paper is often used in general current transformers, and transformers are less used.

4) Wrapped insulation paper: Wrapped insulation paper is used as the base paper of the gluing paper. The gluing paper is used to wind the insulating cylinder (tube) and the capacitive bushing. Its characteristic is that the water absorption height is higher than the cable paper and lower than the impregnated paper. The gluing paper is divided into single-sided or double-sided glue (phenolic or epoxy resin), which is cured at low temperature. When the gluing paper is used to roll the paper cylinder or press the laminated product, the glue is finally cured by heating and pressurizing. The roll is generally made of single-sided glue paper, and the pressed glue paperboard is double-sided glue paper. In addition, there is also diamond-shaped dot glue paper (grid-shaped dot glue paper), which is used for interlayer insulation of oil-impregnated foil-wound coils. After curing, it ensures the adhesion between the insulation and between the insulation and the foil, enhances the strength and has good oil permeability.
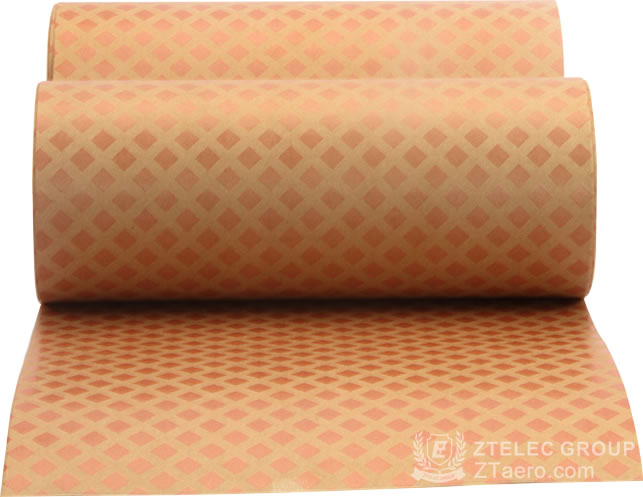

Among the conventional transformer insulation papers, cable paper, crepe paper and diamond-shaped dotted paper are more commonly used. They are used in transformers as inter-turn insulation, inter-layer insulation, lead binding, etc. Usually, the price difference of various types of insulation paper is not too large, about 20 yuan/kg.
1.4 Electrical composite materials
Electrical films and electrical composite materials have excellent dielectric properties and are both thin sheet insulation materials. Electrical films include polyester films and polyimide films, which can also be used as wire insulation, inter-layer insulation, etc. in transformers. Electrical composite materials are composite products made by bonding fiber materials on one or both sides of the film. They can be used as inter-layer insulation in transformers, especially in the foil winding coils of dry transformers. Low-voltage coils usually use composite materials pre-impregnated with resin as inter-layer insulation. Commonly used composite materials include DMD, GHG, etc.
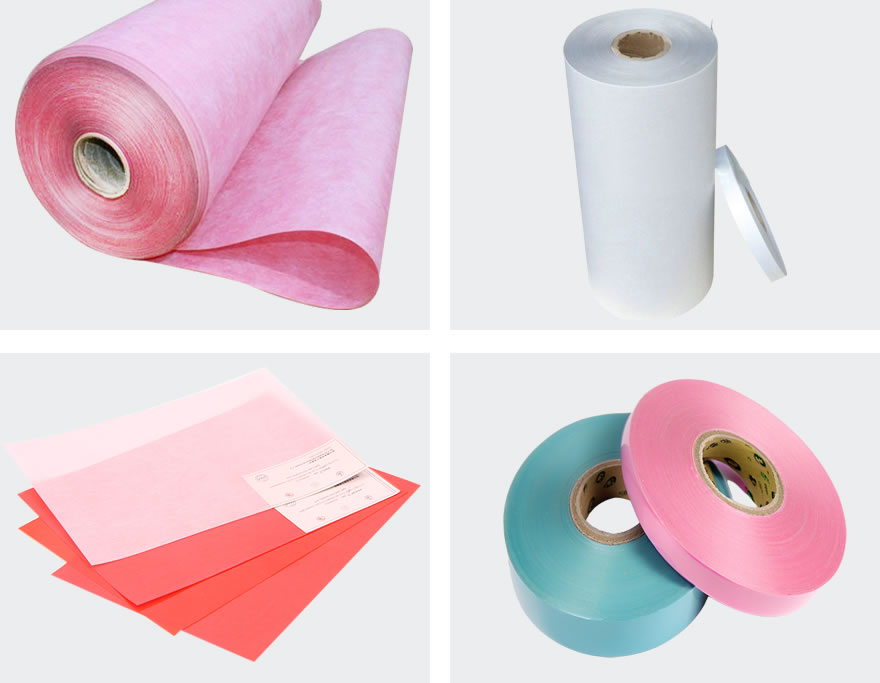

The full name of DMD is polyester film polyester fiber non-woven fabric soft composite material, which is divided into pre-impregnated resin DMD and non-pre-impregnated DMD. It is a three-layer soft composite material made by pasting polyester fiber non-woven fabric (D) on both sides of a layer of polyester film (M). DMD has excellent electrical insulation, heat resistance, mechanical strength and excellent impregnation. Non-prepreg DMD can be used as interlayer insulation for oil-immersed transformers, and prepreg DMD can be used as interlayer insulation for low-voltage foil-wound coils of F-class dry-type transformers. Its specific performance indicators are shown in the following table:
GHG is a polyimide film pre-impregnated H-class resin glass fiber soft composite material. It is a three-layer soft composite material made by pasting glass fiber cloth (G) on both sides of a layer of polyimide film (H). Compared with DMD, it has better heat resistance and can be used for interlayer insulation of low-voltage foil-wound coils of H-class insulation dry-type transformers.
NHN is a polyimide film polyaramid fiber paper soft composite material. It is made of polyaramid fiber paper (Nomex) bonded on both sides of polyimide film with H-class adhesive. NHN is currently the highest-grade thin-layer insulation material with excellent heat resistance, good dielectric properties, low water absorption and excellent moisture resistance. It belongs to H-class insulation material and can be used for interlayer insulation of H-class dry-type transformers. Its specific performance parameters are shown in the following table:
1.5 Insulation paperboard
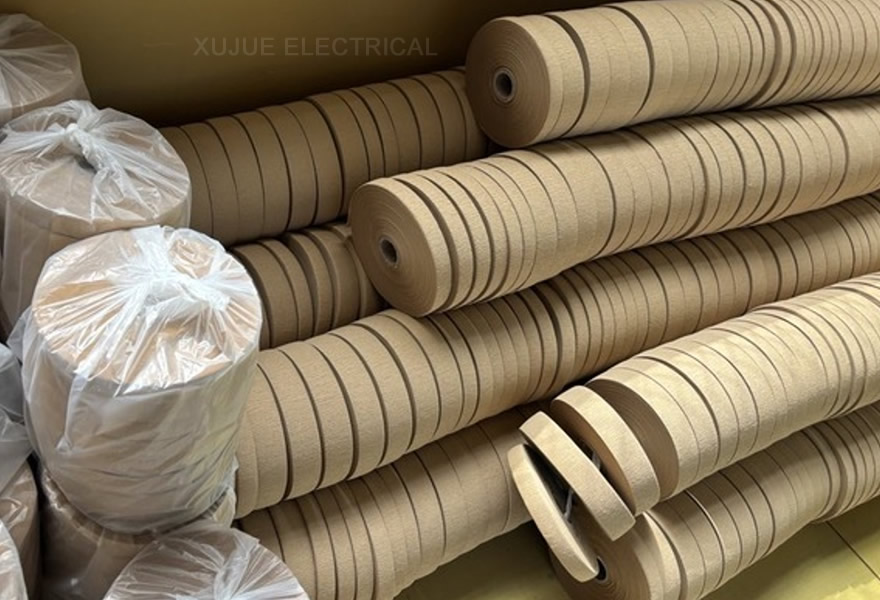
Insulation paperboard is made of pure sulfate wood pulp papermaking. It can be used for oil gap pads, oil gap support bars, partitions, paperboard tubes, corrugated paper, iron yoke insulation, clip insulation and end insulation winding pressure plates of pancake windings. Its common thickness is 1.0mm, 1.5mm, 2mm, 3mm, 4mm, 6mm. Insulation paperboard is divided into low-density paperboard, medium-density paperboard and high-density paperboard according to density. Low-density paper is usually called T3 soft paperboard, with a density between 0.75g/cm3 and 0.9g/cm3. It has low strength and is often used for bending parts or making stretching parts after wetting, such as formed angle rings, ring-shaped parts and soft paper tubes. Low-density paperboard has high oil absorption and good formability, but poor mechanical properties; medium-density paperboard is usually called T1 paperboard, with a density of 0.95g/cm3 to 1.15g/cm3, used as support strips and pads, etc. High-density paperboard is usually called T4 cardboard, with a density of 1.15g/cm3 to 1.3g/cm3, used as insulating paperboard tubes, insulating pressure plates and end rings, etc. In the oil-board spacing structure composed of multi-layer paper tubes of high-voltage coils, corrugated paperboard can also be used instead of paperboard stays to form oil gaps, which can save materials while ensuring insulation performance.

1.6 Polypropylene film
Polypropylene film is made by extruding a thick sheet of polypropylene resin (PP) and directional stretching. Its characteristics are: 1) Low density, can be stretched to 0.06mm or even thinner, its density is 0.89g/cm3~0.92g/cm3. 2) It has good electrical properties and chemical stability, relative dielectric constant is 2~2.2, and breakdown pressure is greater than 150MV/m; 3) It has good mechanical properties, and its tensile strength is greater than 100MPa; 4) It can be used for a long time at 125℃ and belongs to Class E insulation; 5) It is hydrophobic and has strong anti-water absorption ability, and can be used for wire insulation of oil-immersed transformers.
1.7 Other insulating materials
Transformer oil and insulating paper are the main insulating materials for oil-immersed transformer coils, while resin, insulating paper and composite materials are the main insulating materials for dry-type transformer coils. In addition to these materials, the following insulating materials are also commonly used in transformers: (laminated wood, laminated board, insulating paint, insulating glue, cotton cloth tape, shrink tape, weftless tape, etc.)

1) Laminated board: Electrical laminated products are insulating materials with a layered structure made of paper, cloth and wood veneer as the base material, impregnated (or coated) with different adhesives, and hot pressed (or rolled). According to the requirements of use, laminated products can be made into products with excellent electrical and mechanical properties and heat resistance, oil resistance, mildew resistance, arc resistance and corona resistance. Laminated products mainly include laminated boards, laminated wood, laminated tubes, rods, capacitor bushing cores and other special profiles. The performance of laminated products depends on the properties of the base material and adhesive and their molding process. According to the different raw materials and adhesives, laminates are divided into insulating laminates (paperboard, used for oil-fired transformers), phenolic laminated paperboard (commonly known as bakelite, paperboard impregnated with phenolic resin, used for oil-fired transformers), phenolic laminated cloth board (cotton cloth impregnated with phenolic resin, commonly used for oil-fired transformers), epoxy glass cloth board (glass fiber cloth with epoxy resin as adhesive, can be used for F-class dry transformers or oil-fired transformers), modified diphenyl ether glass cloth board (glass fiber cloth with modified diphenyl ether resin as adhesive, can be used for H-class dry transformers), bismaleimide glass cloth board (glass fiber cloth with bismaleimide resin as adhesive, can be used for H-class dry transformers). Laminated boards usually have good mechanical strength and insulation properties, and are often used as core clamp insulation, external support parts, etc. in transformers.
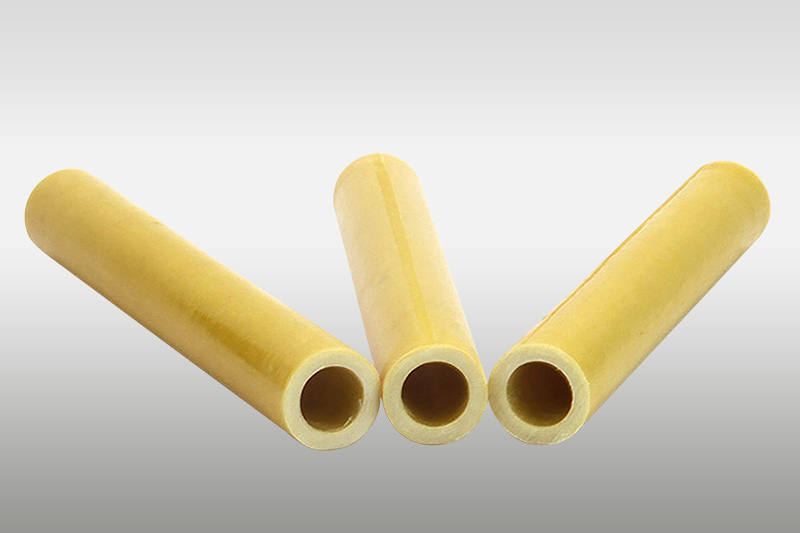
2) Insulating cylinder (tube): The insulating cylinder in the transformer is mainly used between the inner and outer coils, between the coil and the core, and used for the coil lining skeleton. The wire is directly wound on the insulating cylinder. At the same time, the insulating cylinder can also be used for main insulation, increasing the number of main insulation oil gaps and enhancing insulation. According to different materials, the insulation tube is generally divided into phenolic paper tube (commonly used in oil-fired transformers), epoxy glass cloth tube (commonly used in oil-fired transformers or F-class dry transformers), modified diphenyl ether glass cloth tube (commonly used in H-class dry transformers), fiberglass tube (commonly used in H-class dry transformers), bismaleimide glass cloth tube (commonly used in H-class dry transformers), etc.
3) Laminated wood: Electrical laminated wood is made of high-quality hardwood, such as birch, beech, etc., which is steamed twice at 70℃~80℃ to remove the wood acid and grease of the wood itself, and then cut into 1~3mm veneers. After drying, it is coated with resin adhesive, pre-cured, and repeatedly assembled and stacked. It has good insulation strength and mechanical strength and can be used as pads, corner rings, etc. in oil-fired transformers.
4) Binding tape: Transformer binding tape includes cotton cloth tape, tightening tape, mesh semi-dry weftless tape, glass cloth tape, polyester tape, etc., which are used for binding and tightening of iron cores and coils.
Leave us a message to get quotation and sample!
If you are interested in our products,, please send us a message and we will contact you as soon as we receive it. Email: info@ztaero.com whatsApp: +8616650273778
Releated News
- 03-11 2026Drive Motor Insulation Materials: FR4, G10 & NMN
- 03-10 2026Crepe Paper Tube for oil Transformer
- 03-09 2026Epoxy Fiberglass Insulation Sheets for Lithium Battery Packs (FR4 / G10 / 3240)
- 03-06 2026Types and Selection of Transformer Laminated Wood
- 03-05 2026Insulation Raw Materials — Epoxy Resin Price Increase
- 03-05 2026NMN Flexible Insulation Material for Motor Winding