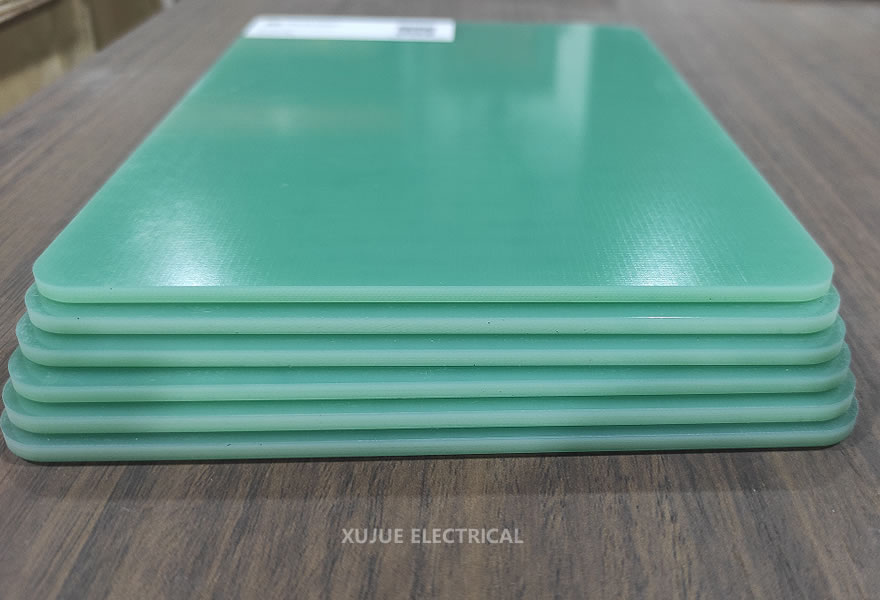
G10 epoxy board green and black difference
Differences Between Green and Black G10 Epoxy Board The green and black versions of G10 epoxy board (glass fiber rei...
Differences Between Green and Black G10 Epoxy Board
The green and black versions of G10 epoxy board (glass fiber reinforced epoxy laminate) are virtually identical in their fundamental material composition and core properties such as mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance. Their main differences lie in the source of color, subtle variations in certain non-critical properties, and resulting application preferences:
Source of Color:
Green G10 board: This is the most classic and common color. Green typically comes from the natural hue of the glass fiber cloth itself after impregnation and curing in epoxy resin (glass fiber cloth is usually a pale yellowish-green or natural color), or sometimes small amounts of green pigment are added to enhance and standardize the color. It is the “base” color.
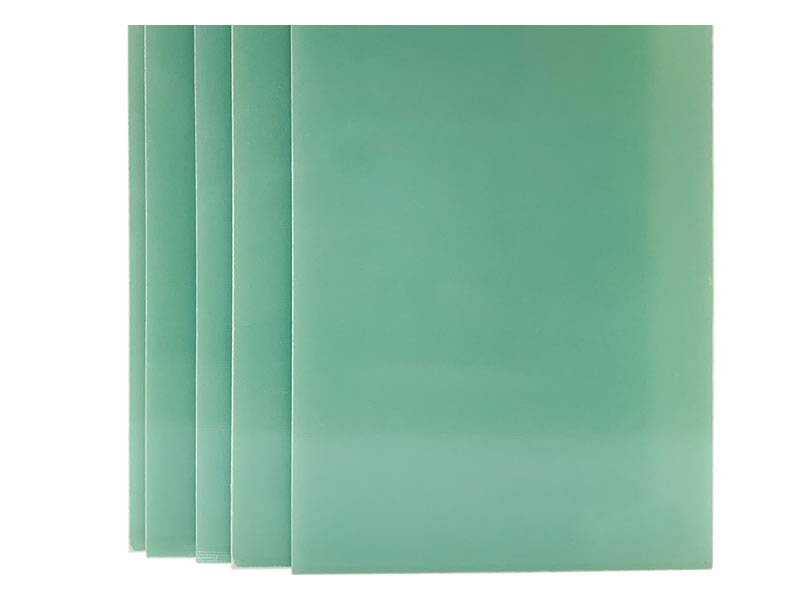

Black G10 board: Black is achieved by adding black pigment (typically carbon black) to the epoxy resin. This is an additive coloration.
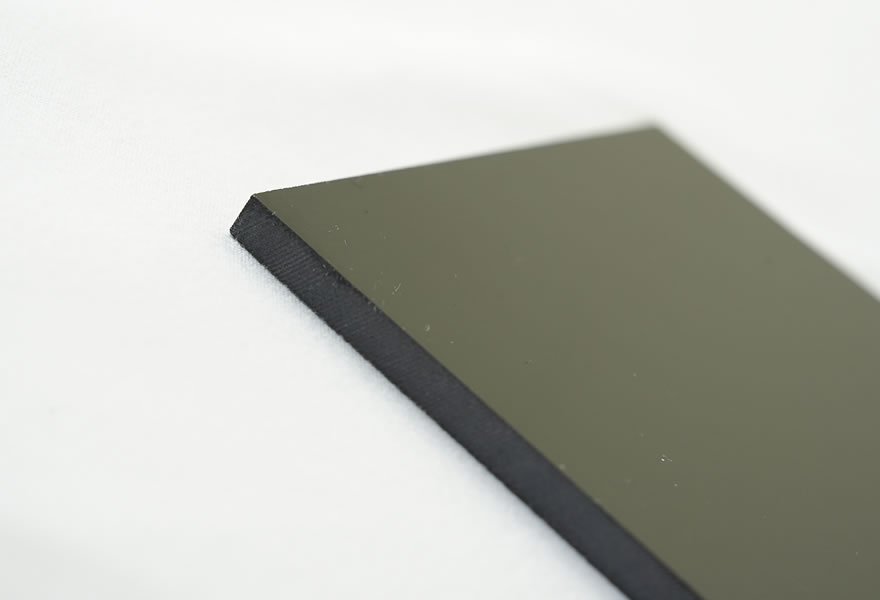

Impact of Additives (Subtle Performance Differences):
Mechanical Properties: The addition of carbon black pigment could theoretically have an extremely minor negative impact (filler effect) on ultimate mechanical properties (like tensile strength, flexural strength). However, this difference is usually negligible in practical engineering applications and both colors meet G10 material specifications. For the vast majority of applications, their strength is equivalent.
Thermal Conductivity: Carbon black is a good thermal conductor and heat absorber. Therefore, black G10 typically has a slightly higher thermal conductivity than green G10 and absorbs thermal radiation more effectively. This gives black G10 a slight advantage in applications requiring heat dissipation (e.g., as an insulating spacer under power components).
Heat Reflectivity: Correspondingly, green G10 usually has slightly higher heat reflectivity than black G10.
Machinability: When cutting or milling, the edges or machined surfaces of black G10 may sometimes show the internal lighter color (white or pale yellow of the glass fibers) more readily, creating a color contrast, whereas this contrast might be less noticeable on the green version. This does not affect physical properties.
Appearance and Opacity:
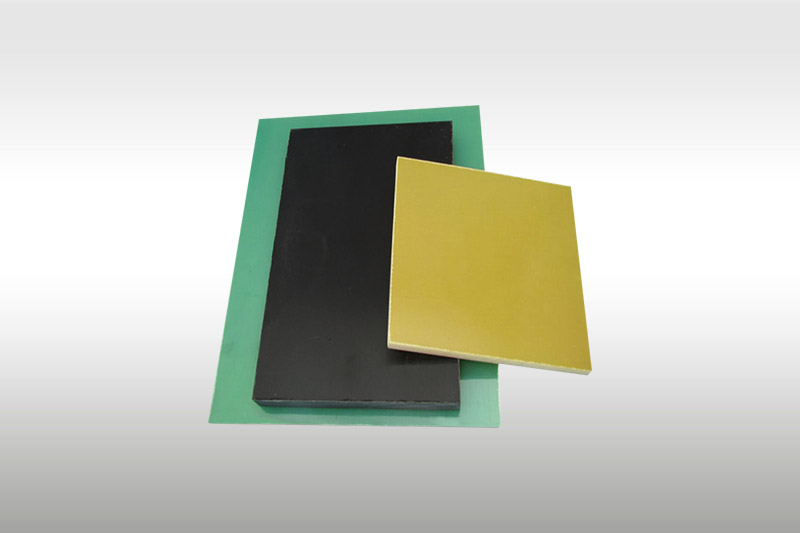
Appearance: This is the most obvious difference. Green is the industrial standard color, while black offers a more modern, professional, or discreet appearance.
Light Transmission: Green G10 is typically semi-translucent (especially thinner sheets), showing blurred light transmission under strong light. Black G10, due to the carbon black, is completely opaque. This is an advantage in applications requiring light blocking (e.g., certain optical or electronic enclosures).
Application Preferences:
Green G10: The most versatile and common. Widely used for electrical insulation (terminal boards, insulating spacers, transformer barriers), structural supports, model making, test fixtures, etc. Preferred when color is not critical or a traditional industrial appearance is desired.
Black G10:Aesthetic Requirements: Used where a black appearance is needed to match product design, enhance aesthetics, or appear more professional (e.g., panels for high-end audio equipment, instrument housings).
Thermal Considerations: When its slightly better thermal conductivity/heat absorption is beneficial (e.g., insulating heat spreaders under high-power components).
Light Blocking Requirement: Applications requiring complete opacity to prevent light transmission.
Reduced Visible Contamination: In certain environments, dust or stains might be less noticeable on a black surface compared to a light green one.
Green G10 board VS Black G10 board:
| Characteristic | Green G10 | Black G10 |
|---|---|---|
| Color Source | Natural glass cloth + possible minor green pigment | Carbon black pigment added to epoxy resin |
| Core Properties | Excellent (Mech. strength, insulation, chem. resist.) | Excellent (Essentially same as green) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Standard | Slightly Higher (Carbon black effect) |
| Heat Absorption | Standard | Slightly Better (Carbon black effect) |
| Heat Reflectivity | Slightly Higher | Standard |
| Light Transmission | Typically Semi-translucent | Completely Opaque |
| Appearance | Traditional industrial green | Modern, professional black |
| Primary Applications | General: Insulation, structural support, models, fixtures | Black appearance, heat dissipation needs, light blocking needs, aesthetic requirements |
Core Conclusion: Choosing between green or black G10 primarily depends on appearance preference, specific thermal dissipation needs, or light blocking requirements. Regarding critical electrical insulation performance and mechanical strength, there is no fundamental difference; both are high-performance engineering materials. If color and light transmission are not concerns, green is typically the more economical and common choice. If a black appearance, better heat dissipation, or complete opacity is needed, then choose black G10.
Leave us a message to get quotation and sample!
If you are interested in our products,, please send us a message and we will contact you as soon as we receive it. Email: info@ztaero.com whatsApp: +8616650273778
Releated News
- 02-10 20262026 Spring Festival Greeting | XUJUE ELECTRICAL
- 02-06 2026G11 Epoxy Sheet for Generator Slot Insulation
- 02-05 2026Fiberglass cloth Prices Continue to Rise | Sheet Product Prices May Be Adjusted
- 02-03 2026Epoxy Pultruded Rod Applications | Electrical Insulation & Structural Support
- 02-02 2026Common Insulation Materials Comparison for High- and Low-Voltage Switchgear
- 01-31 2026Differences Between G11 Epoxy Sheet and EPGC308